In this post, we will take a look at some notable forks of Slackware Linux. Recently, I published a post that honoured Slackware Linux, one of the oldest surviving Linux distributions. While Slackware is appreciated by advanced Linux users for its simplicity, stability and adherence to UNIX philosophies, it is often considered as a “Hard to master” distribution for beginners. Possible reasons include its minimalist approach, less out-of-the-box functionality, and limited automated tools compared to modern Linux distributions.
This blog post delves into notable forks of Slackware Linux – Salix OS, Zenwalk GNU/Linux, Porteus, and Slacko Puppy Linux. These notable forks of Slackware Linux have retained stability and simplicity. They have provided features like automated package management, graphical tools and desktop optimization while still staying compatible with the core Slackware ethos of being a clean, minimalist UNIX-like operating system. Each distribution has unique features and specific use-cases, illustrating the versatility of Linux distributions. Whether it’s simplicity, speed, portability, or low system requirements, there’s a Slackware variant to meet your needs.
यह ब्लॉग पोस्ट Slackware Linux के महत्वपूर्ण forks – Salix OS, Zenwalk GNU/Linux, Porteus, और Slacko Puppy Linux पर विचार करता है। इन महत्वपूर्ण Slackware Linux के forks ने स्थिरता और सरलता को बनाए रखा है। इन्होंने स्वचालित पैकेज प्रबंधन, ग्राफिकल उपकरण और डेस्कटॉप अनुकूलन जैसी सुविधाएं प्रदान की हैं, जबकि वे मूल Slackware नीति के साथ संगत रहते हैं – एक स्वच्छ, न्यूनतम UNIX-प्रकार का ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम होने की। प्रत्येक वितरण में अद्वितीय विशेषताएं और विशिष्ट उपयोग मामले हैं, जो Linux वितरणों की विविधता को दर्शाते हैं। चाहे यह सरलता, गति, पोर्टेबिलिटी, या कम सिस्टम आवश्यकताएं हों, एक Slackware variant आपकी जरूरतों को पूरा करने के लिए है।
या ब्लॉग पोस्टमध्ये Slackware Linux च्या उल्लेखनीय forks – Salix OS, Zenwalk GNU/Linux, Porteus, आणि Slacko Puppy Linux वर विचार केला जातो. ह्या Slackware Linux च्या उल्लेखनीय forks मध्ये स्थिरता आणि सोप्यापणा जतन केले आहे. त्यांनी स्वयंसेवी पॅकेज प्रबंधन, चित्रपटीय साधने आणि डेस्कटॉपसाठी अनुकुलित करणे यामुळे महत्त्वाच्या सुविधा पुरविण्यात आली आहेत ह्या म्हणजे आपल्याला चांगले उपयोगक्षमता आणि खालीलप्रमाणे लक्षात घेतलेल्या Slackware आधारभूत सिद्धांतांचा ठेव दिला जातो – स्वच्छ, न्यूनतम UNIX-प्रकारचा ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम. प्रत्येक वितरणात एकूण वैशिष्ट्ये आणि विशिष्ट वापर-प्रकरणे आहेत, ज्यामुळे Linux वितरणांची विविधता दर्शवितात. सोपासा, वेगवान, पोर्टेबल, किंवा किंवा किंवा कमी सिस्टम आवश्यकता, तुमच्या गरजांचा एक Slackware variant आहे.
Introduction
The open-source nature of Linux allows for the creation of diverse distributions or ‘forks’ to cater to specific user needs. A fork is essentially a variant of the original software, made by copying the source code and modifying it. Slackware, one of the oldest surviving Linux distributions, is known for its simplicity, stability, and adherence to Unix-like design principles.
When we merge the two thoughts: using Slackware Linux, we get the core stability and architecture of Slackware; while adding tweaks, tools and modifications we can improve ease of use and functionality. A fork of the base Slackware Linux distribution can help us achieve just that. Several notable forks of Slackware Linux have emerged over the years, each with unique features and distinct use cases. This blog post focuses on Salix OS, Zenwalk GNU/Linux, Porteus, and Slacko Puppy Linux, showcasing their unique features and how they’ve evolved from their Slackware roots. I had mentioned these forks in the mega post on Slackware Linux which was published previously.
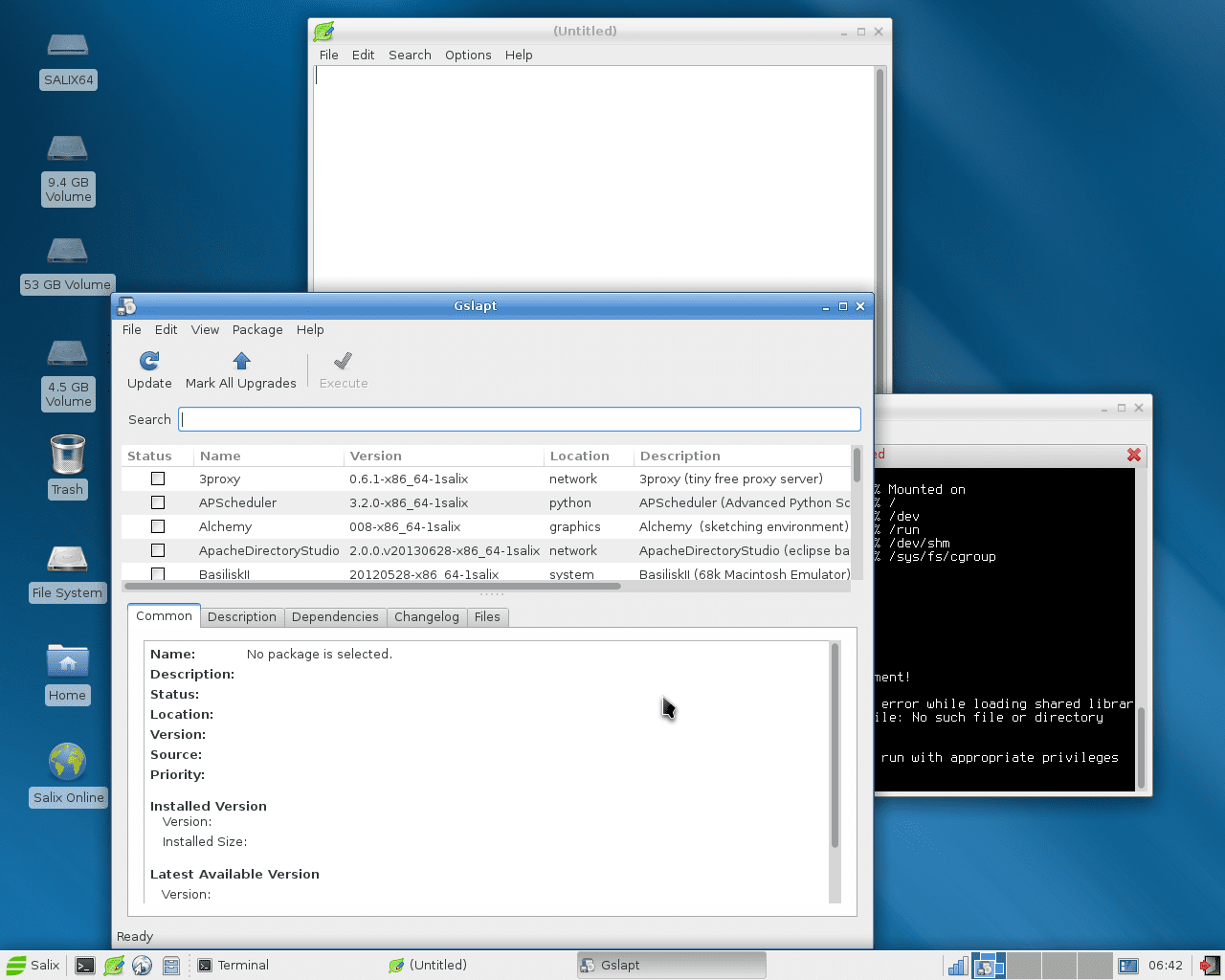
GSlapt for SalixOS – Front end for Slapt-get. Dec 2017
Notable Forks of Slackware Linux
Salix OS
Salix OS is a fork focused on retaining maximum compatibility with Slackware while adding desktop-focused improvements. Salix OS prides itself on simplicity, speed, and ease of use. Salix aims to reduce user workload while maintaining maximum compatibility with Slackware. This Linux distribution is optimized for desktop usage, supporting both 32-bit and 64-bit architectures. Salix boasts high-quality package repositories with dependency support, fast package tools, and fully localized system administration tools. Aptly described as a distribution for ‘lazy Slackers’, Salix simplifies the Slackware installation process and offers a pre-configured desktop environment and applications.Key features include:
- Uses Slackware’s package management system for stability
- Comes preconfigured with Xfce, KDE, LXDE or Fluxbox desktop environments
- Simple graphical system administration tools
- Installation process simplified compared to Slackware
- Good for Linux users who want a no-frills system with some added polish
Zenwalk
Zenwalk aims to be a modern, multi-purpose Slackware-based distribution. It supports both beginner and advanced users, offering a focus on internet applications, multimedia, and programming tools. Initially called Minislack, Zenwalk uses the netpkg package management system, compatible with Slackware’s .tgz package format. Zenwalk is a 64-bit “pure” Slackware system, incorporating post-install configurations, optimizations, and out-of-box tweaks for a ready-to-use desktop environment.Key highlights:
- Focuses on internet, multimedia and programming apps
- Compatible with Slackware packages
- Uses custom netpkg package manager
- Switched from KDE to lightweight Xfce environment
- Includes various tweaks and optimizations for desktop usage
- Retains Slackware’s simplicity and stability
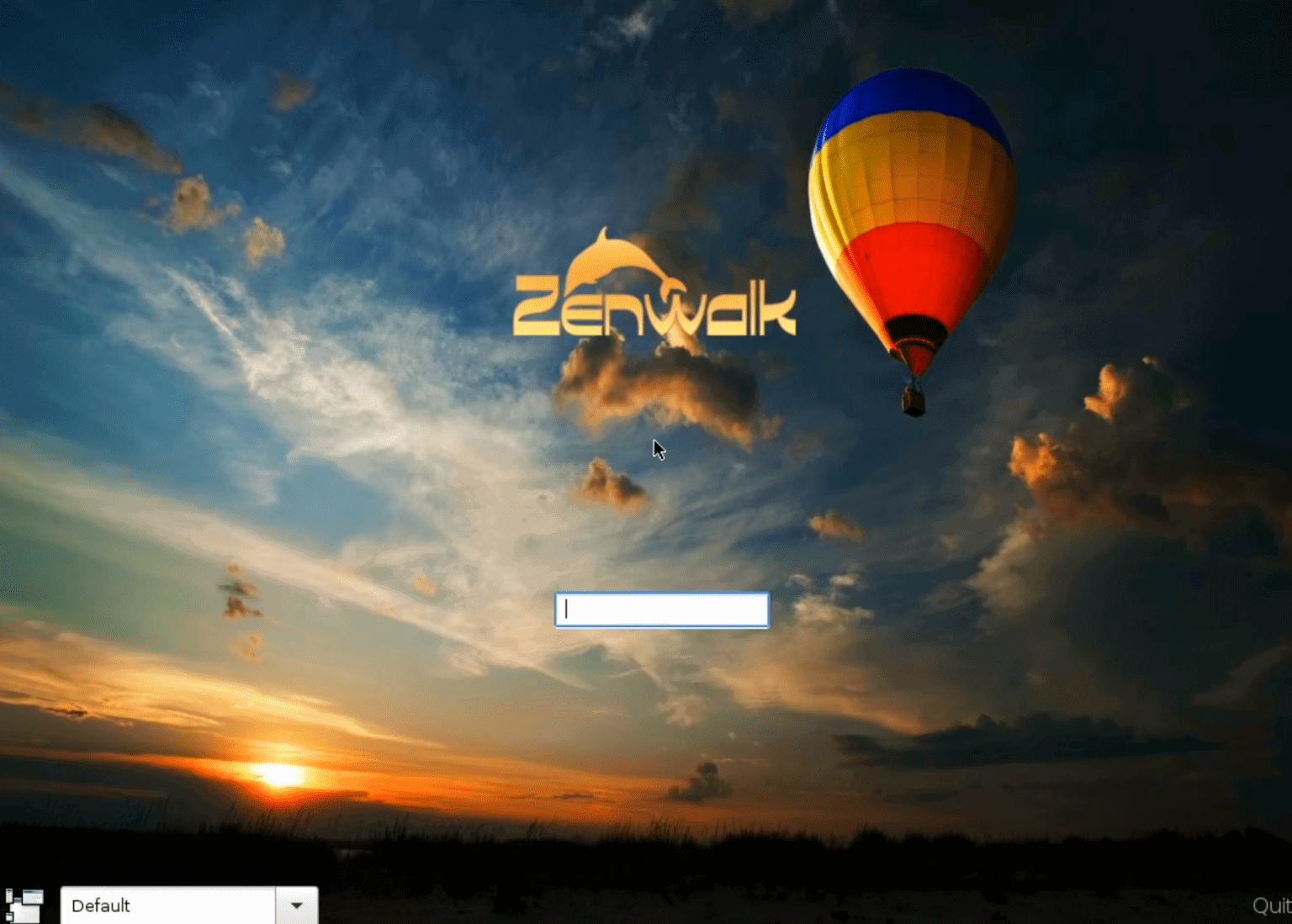
Zenwalk Linux, one of the Notable Forks of Slackware Linux
Porteus OS
Porteus is a unique modular Slackware fork focused on portability and speed. Porteus is designed to be fast and lightweight with a small footprint. Ideal for running from USB flash drives, flash cards, or CDs, Porteus also supports a ‘frugal’ install on hard disks. The system offers a modular design for easy application management and includes a dependency-resolving package manager with access to Slackware repositories. Porteus aims to provide a portable, fast, and light operating system that boots directly in less than 15 seconds.Features include:
- Extremely small footprint – under 300MB
- Can run from live media like USB drives without installation
- Modular system allows adding/removing apps easily
- Custom dependency-resolving package manager
- Choice of multiple desktop environments (Xfce, LXQt etc.)
- Fast boot time – as little as 15 seconds
Slacko (Puppy Linux)
Slacko, built from the Woof-CE build system, is compatible with the binary packages of Slackware 14.1. This operating system is available in both 32-bit and 64-bit versions and is designed to be light, suitable for low-end machines and older hardware components. Slacko Puppy boasts binary compatibility with Slackware and access to the Slackware and Salix repositories.
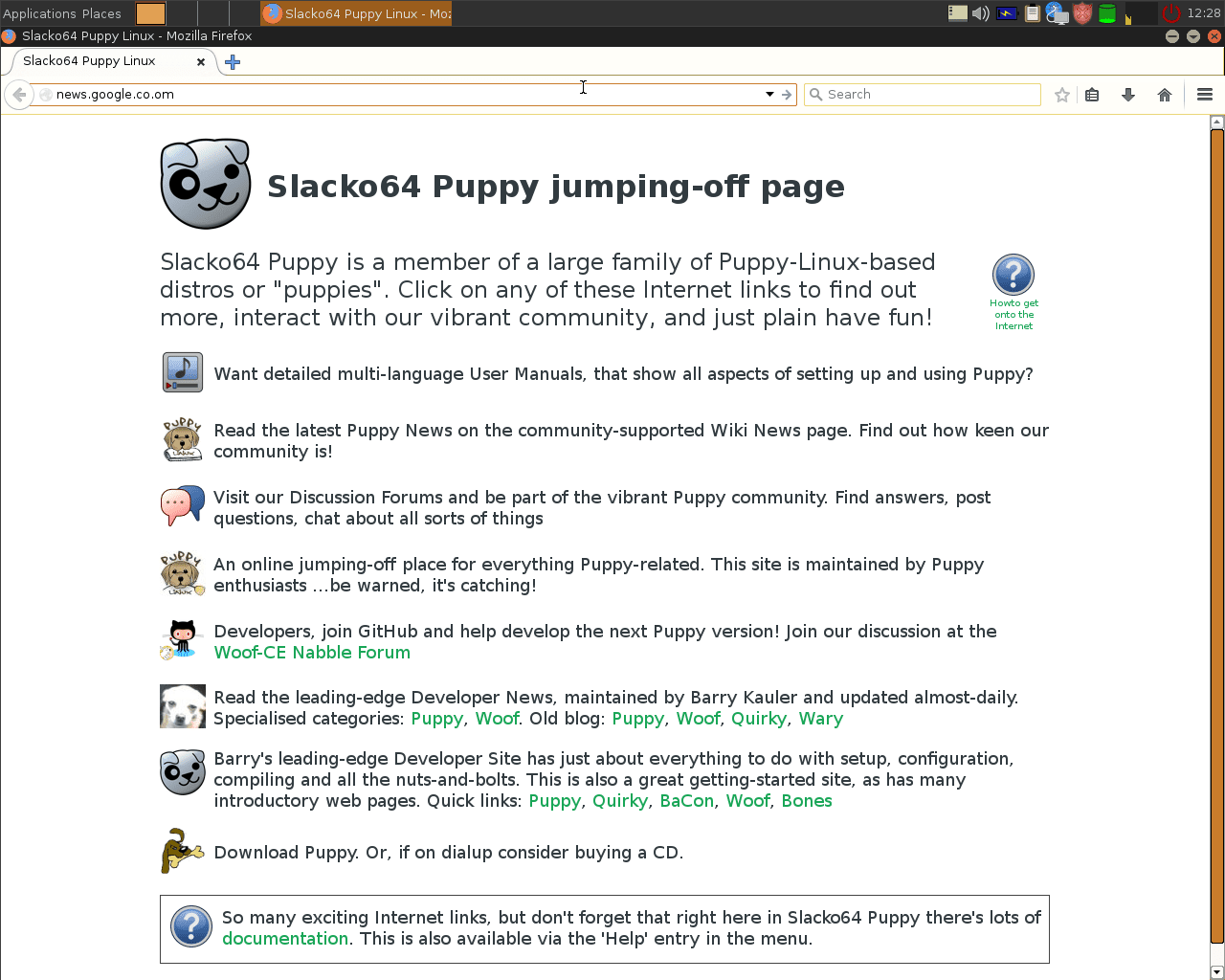
Screenshot showing Slacko Linux, Dec 2017.
Comparing features of Notable Forks of Slackware
Despite the growing number of forks, Slackware remains the core inspiration and source for these diverse Linux experiences. Its philosophy of simplicity and stability has influenced many other distributions, and its community continues to thrive and contribute to the open-source world.
Fun fact: One of the earliest forks of Slackware was SUSE Linux, which was created in 1994. SUSE was initially based on Slackware, but it has since evolved into its own unique distribution, with a focus on enterprise and commercial use.
| Fork of Slackware | Features | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Slackel | An independent fork of Slackware designed for beginners and experienced users alike. It offers a simple installation process and includes additional tools for managing your system. |
| 2 | SalixOS | A lightweight Slackware-based distribution that focuses on ease of use and speed. It uses the XFCE desktop environment and offers a streamlined installation process. |
| 3 | Porteus | A live CD/USB version of Slackware that allows you to run the operating system without installing it on your hard drive. It is highly customizable and offers a wide range of applications out of the box. |
| 4 | ZenSlack | A Slackware-based distribution that aims to provide a minimalistic and simple computing experience. It uses the Openbox window manager and includes a few pre-installed applications. |
| 5 | ZipSlack | A lightweight and portable Slackware-based distribution that can run from a USB drive. It includes a minimalistic interface and a few pre-installed applications. |
| 6 | Austrumi Linux | A minimalist GNU/Linux distribution based on Slackware Current. It is a bootable live CD Linux Distribution created and maintained by a group of programmers from the Latgale region. Austrumi is known for its small size and nimbleness. It is also noted for its unique features that set it apart from other systems designed for older hardware. |
| 7 | Absolute Linux | A lightweight Linux distribution based on Slackware Linux, designed to work efficiently on older hardware. It is designed for everyday use, including internet browsing, multimedia, and document handling. The default window and file managers are IceWM and ROX-Filer, and it comes with many pre-installed programs for image editing, office software, and other tools. It uses a graphical frontend to XPKGTOOL and also bundles Gsplat, a Graphical frontend to Slapt-get which works similarly to Apt-get. It uses its own repositories which provide its own as well as packages from Slackware. |
| 8 | VectorLinux | My personal favourite fork was VectorLinux, which was created in 1999 and is known for its speed and lightweight design. This project seems to be inactive. The last official release, Version 7.1, was made in 2015, and their official website has been down for a while |
Other Forks of Slackware
Some other forks like Absolute Linux, Vector Linux, SLAX, Bluewhite64, etc. retain Slackware’s core strengths while adding their own tweaks to improve ease of use and functionality. They cater to niche audiences who prefer the UNIX-style simplicity of Slackware. A noteworthy fork of Slackware Linux is Slackel, a Linux distribution and live CD based on Slackware Linux and Salix. It is fully compatible with both. It uses the current version of Slackware and the latest version of the KDE desktop. The Slackel disc images are offered in two different forms for full installation and as a live disk.
Distrowatch maintains a list of forks of Slackware.
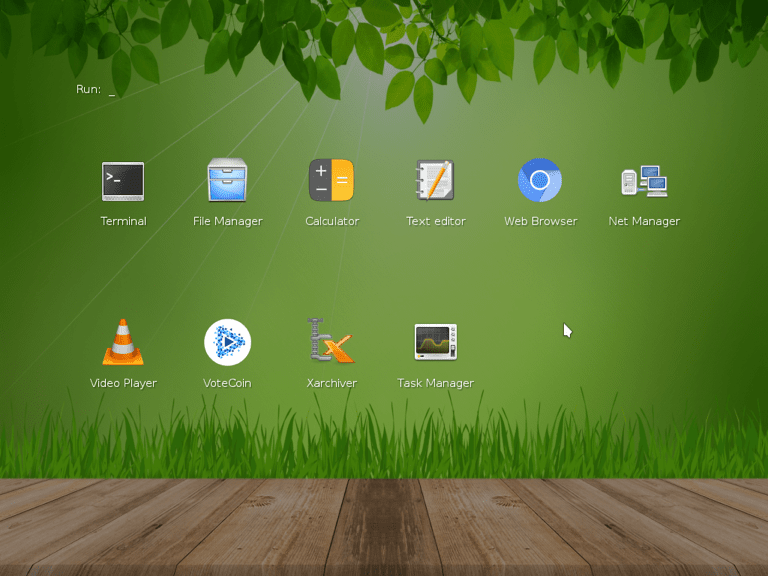
Screenshot of Slax Linux from April 2018. Slax has 2 variations now- debian based, or slackware based.
Slax using Virtualbox. March 2018
Conclusion
Slackware forks allow users to benefit from the stability and architectural strengths of Slackware, while getting added features and tools where the base system is lacking. They continue to keep Slackware relevant for modern Linux users. The notable forks of Slackware linux , each with their distinct features and use cases, show the flexibility and adaptability of Linux distributions. Whether you prioritize speed, simplicity, portability, or minimal system requirements, there’s a Slackware fork that fits the bill. By understanding these forks better, you can make an informed choice about the Linux distribution that best suits your needs.

Logo of Slackware Linux (Source: Quora)


